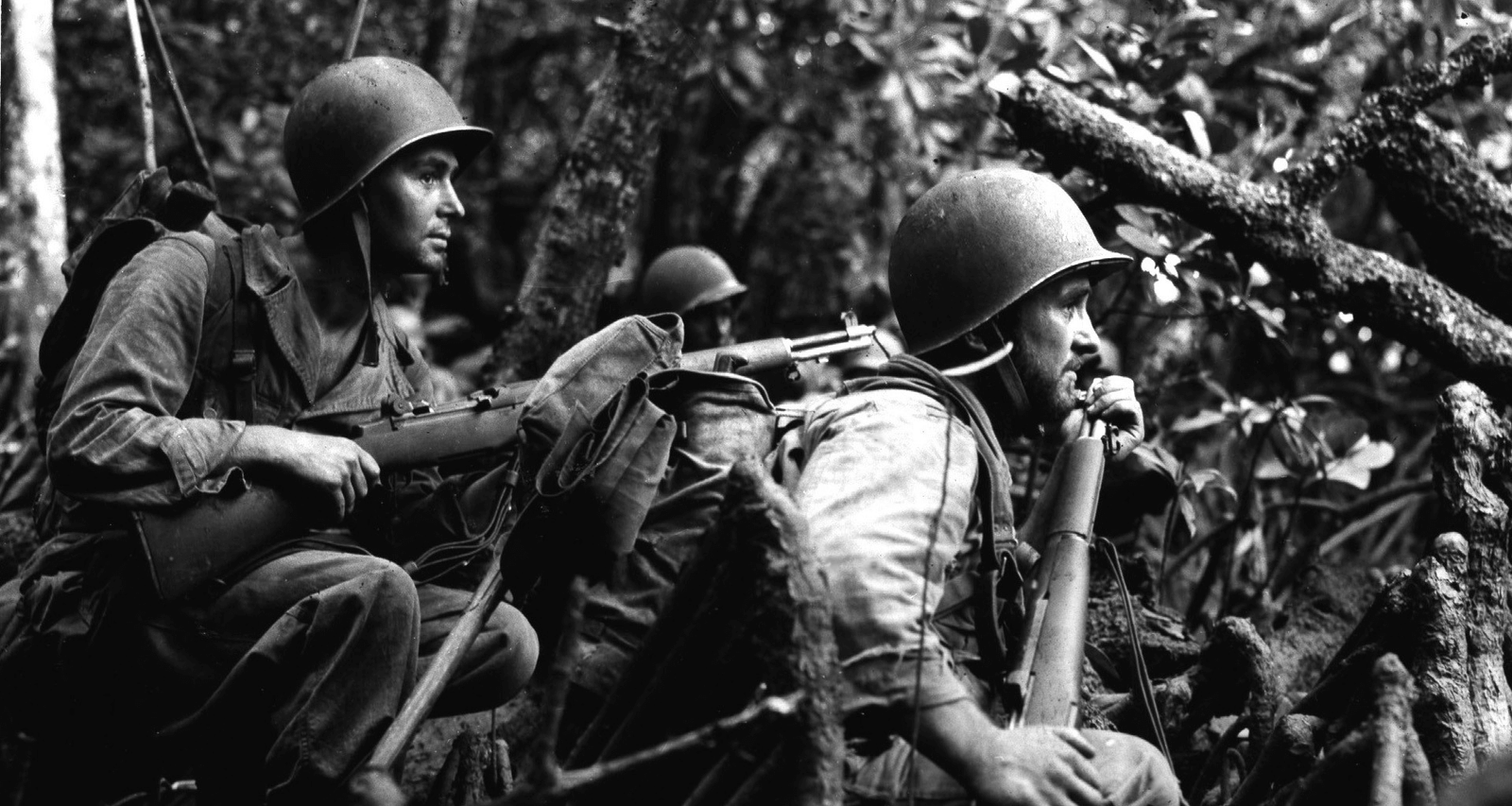
The First World War, also known as the Great War, was a global conflict that lasted from 1914 to 1918. It was one of the deadliest conflicts in human history, with an estimated 16 million military and civilian deaths. This article will explore the causes, major events, and consequences of the First World War.
Causes of the First World War
The immediate cause of the First World War was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary on June 28, 1914, by a Serbian nationalist. However, the underlying causes of the war were much more complex. One of the major causes was the complex system of alliances that had developed in Europe. In the years leading up to the war, European powers formed alliances for protection and security. The two major alliances were the Triple Entente (Britain, France, and Russia) and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy).
Another cause of the war was the arms race that had developed among the major powers. Military technology had advanced rapidly in the years leading up to the war, and countries were eager to have the most advanced weapons and military capabilities. This led to a dangerous buildup of arms and a sense of mistrust and hostility between the major powers.
Major Events of the First World War
The war began on July 28, 1914, when Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. This triggered a chain reaction, with other countries joining the conflict. Germany declared war on Russia and France, and Britain declared war on Germany.
The war quickly became a global conflict, with major battles fought on land, sea, and air. One of the most significant battles was the Battle of the Somme, fought from July to November 1916. It was one of the bloodiest battles in human history, with over one million casualties.
In addition to the major battles, the war also had significant impacts on civilians. The war led to food shortages and economic disruption, as well as the displacement of millions of people.
Consequences of the First World War
The First World War had a profound impact on the world. The war resulted in the collapse of empires and the redrawing of national borders. The Ottoman Empire, which had been in decline for many years, was dissolved, and the Middle East was divided into new states. The war also led to the establishment of new countries, including Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia.
The war also had significant social and cultural impacts. The war had shattered the optimism and confidence that had characterized the pre-war period, and it led to a sense of disillusionment and despair. Many artists and writers responded to the war with works that expressed this sense of disillusionment, including T.S. Eliot’s poem “The Waste Land” and Ernest Hemingway’s novel “A Farewell to Arms.”
In addition to its cultural and social impacts, the war had significant political consequences. The Treaty of Versailles, which was signed in 1919, imposed harsh reparations on Germany and led to the rise of nationalism and resentment in that country. This, in turn, contributed to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the outbreak of the Second World War.
Synoptically, The First World War was a global conflict that had far-reaching consequences. Its causes were complex and rooted in the political and military tensions of the pre-war period. The war had significant impacts on the world, including the collapse of empires, the redrawing of national borders, and the establishment of new countries. The war also had significant social, cultural, and political consequences that shaped the course of the 20th century.

Meet Sir Faisal Amin – a visionary educator and content management expert, who has made a lasting impact in the education sector with his unwavering commitment and passion.